Capsaicin, the active agent in spicy hot chili peppers can reduce pain
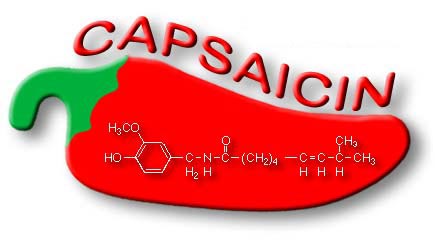 Recent study revealed that capsaicin, the compound that gives chili peppers their fiery flavor can also help in relieving joint and muscle pain. Study indicated that capsaicin flips on nerve-ending receptors that sense both pain and heat.
Recent study revealed that capsaicin, the compound that gives chili peppers their fiery flavor can also help in relieving joint and muscle pain. Study indicated that capsaicin flips on nerve-ending receptors that sense both pain and heat.
Lead researcher, Feng Qin, an associate professor at the university's School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences, said: "The receptor acts like a gate to the neurons. When stimulated it opens, letting outside calcium enter the cells until the receptor shuts down, a process called desensitization."
He added that the analgesic action of capsaicin is believed to involve this desensitization process. However, how the entry of calcium leads to the loss of sensitivity of the neurons was not clear.
The research team concluded that while capsaicin has been used in folk medicines for generations, knowing how it works in relation to PIP2 may lead to developing other analgesics that ease pain without first causing irritation on their own.