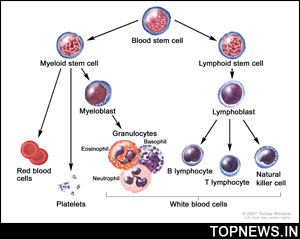
 Washington, April 23 : Researchers at University of British Columbia have identified a `molecular key' that has the potential to increase the success of blood stem cell transplants.
Washington, April 23 : Researchers at University of British Columbia have identified a `molecular key' that has the potential to increase the success of blood stem cell transplants.
Blood stem cell transplants are currently used to treat diseases such as leukemia, Hodgkin''s lymphoma and aplastic anemia.
During the procedure, donor blood stem cells - which can produce red and white blood cells and platelets - are injected into the recipient to produce new blood.